En tant qu’enseignant, vous avez certainement entendu parler de l’évaluation par les pairs et de ses bénéfices.
Alors comment intégrer l’évaluation par les pairs dans vos cours et comment bénéficier au maximum des avantages pédagogiques qu’offre cette pratique.
Nous avons créé cet article pour vous permettre d’avoir quelques exemples d’intégration de l’évaluation par les pairs en fonction de cas d’usage avec ChallengeMe.
Si vous souhaitez en savoir plus sur l’évaluation par les pairs, nous vous invitons à consulter cet article.
N’hésitez pas à consulter également notre article sur les grilles d’évaluation par les pairs
Ce cas d’usage vise à entraîner les étudiants bénéficiant d’un cours magistral mais n’ayant pas la possibilité de s’exercer car la correction serait beaucoup trop chronophage pour l’enseignant : (Ex : 200 copies à corriger pour un enseignant). Ce cas d’usage est d’autant plus pertinent lorsqu’un examen est prévu prochainement car cela permet aux étudiants de «pratiquer» plus régulièrement et de recevoir des feedback pour les aider à progresser.
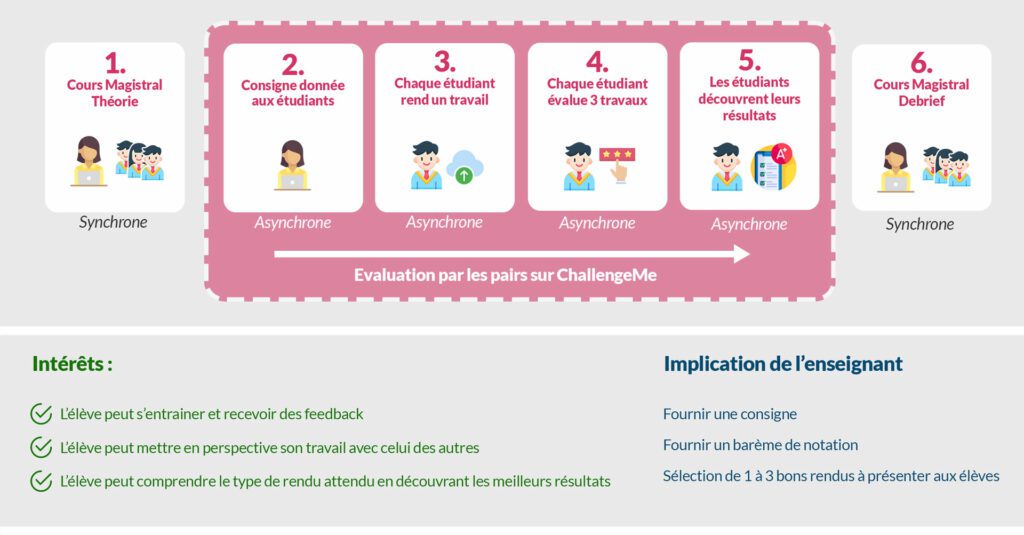
Voici donc la solution que ChallengeMe vous propose pour répondre à ce besoin :
Dans le monde professionnel, nous sommes de plus en plus amenés à donner nos feedback. L’objectif ici est d’apprendre à l’élève à donner un feedback constructif en se focalisant sur différents critères en justifiant chacun d’entre eux.
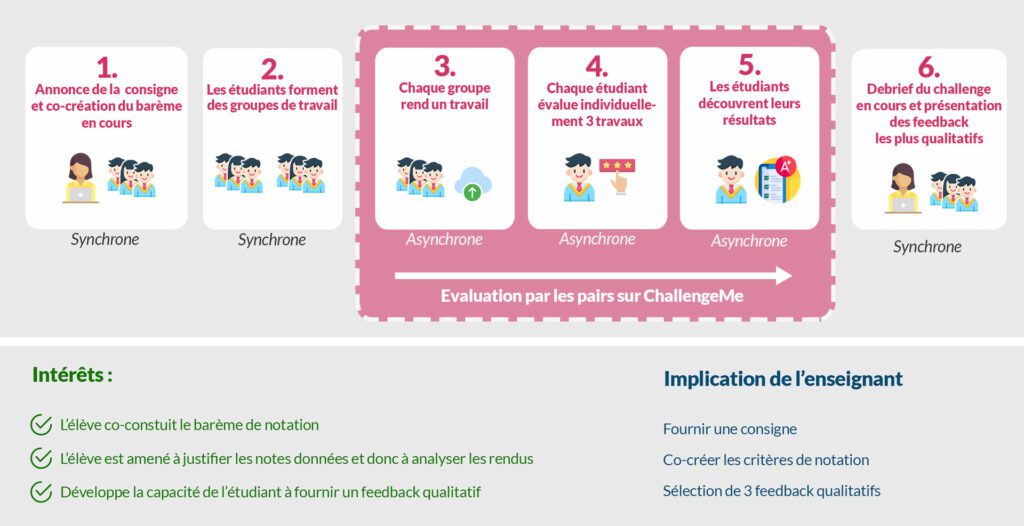
Il peut être intéressant pour l’enseignant d’impliquer les étudiants dans le processus de notation en leur donnant une partie de la responsabilité de la note. Cela permet à l’élève de renforcer ses connaissances puisqu’il sera amené à découvrir les travaux des autres tout en mettant en perspective un certain nombre de critères.
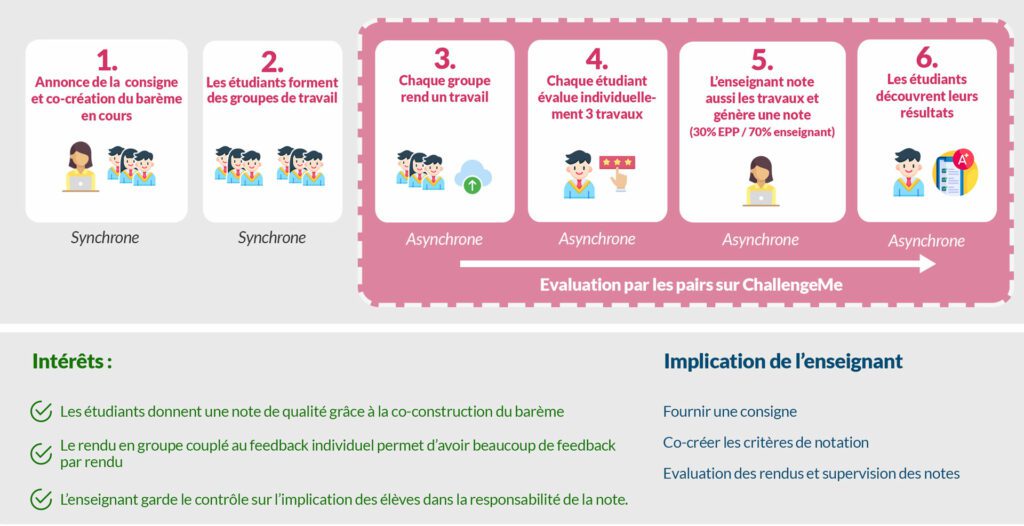
Il est tout à fait possible pour ce cas d’usage de construire la note à 100% via la note de l’EPP si l’enseignant estime que les notes données sont justes. Une pénalité peut être appliquée aux étudiants ayant bâclés l’étape de notation.
Lors de présentations orales, il peut arriver que certains élèves ne soient pas attentifs durant tout le cours dû au niveau d’attention qui leur est demandé. Cela est d’autant plus vrai en période de covid avec des cours en distanciel. L’objectif ici est donc d’impliquer davantage les élèves via une activité ludique.
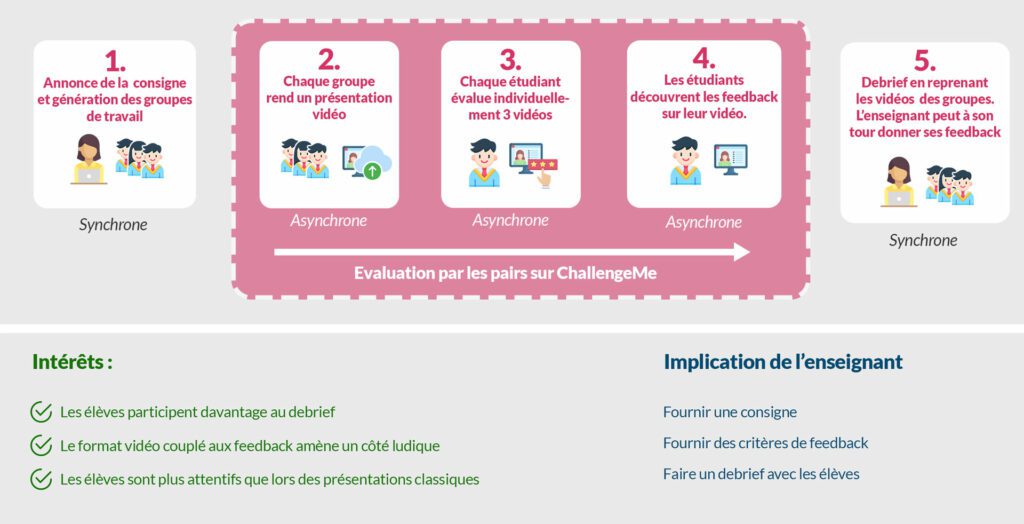
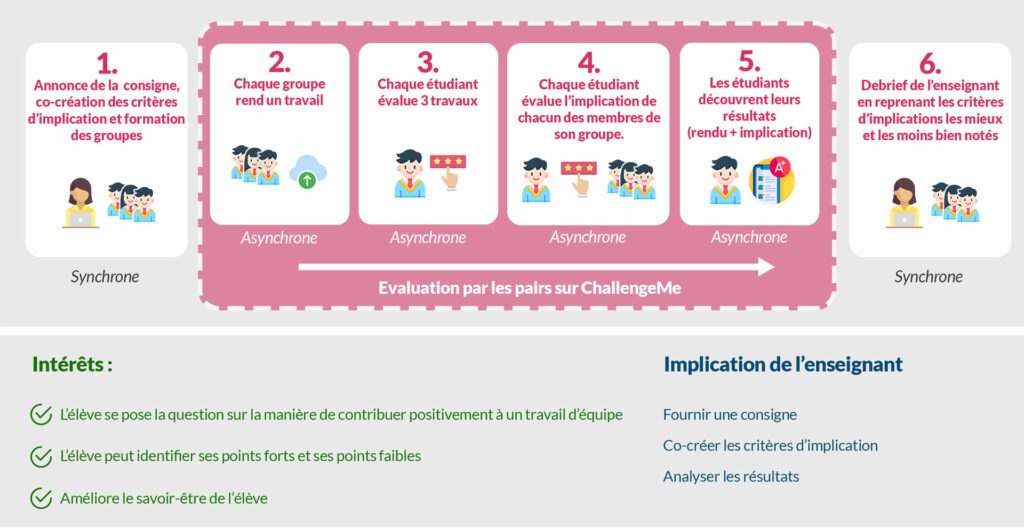
Le travail en équipe n’est pas toujours équitable en termes d’implication. Certains peuvent se reposer sur les autres, d’autres peuvent au contraire imposer leurs idées. L’idée ici est de faire se questionner les élèves sur les différentes façons de contribuer positivement à un travail de groupe.