Je profite de mon intervention chez Burgundy SB avec Stéphane Moriou, l’expert du Feedback, pour vous partager quelques éléments/réflexions.
Dans le monde de l’éducation, le feedback est reconnu comme un élément crucial pour l’amélioration des compétences et la motivation des étudiants. Il ne s’agit pas simplement de corriger des erreurs, mais d’encourager une réflexion approfondie et d’orienter les apprenants vers des objectifs clairs et atteignables. Cet article explore les bonnes pratiques du feedback, en s’appuyant sur les recherches actuelles et les ressources disponibles, dans ChallengeMe, pour les enseignants et les étudiants.
Le feedback joue un rôle central dans le processus d’apprentissage. Il aide les étudiants à comprendre leurs forces et leurs faiblesses, à s’auto-évaluer et à ajuster leurs stratégies d’apprentissage. Selon Hattie et Timperley, le feedback est l’un des facteurs les plus influents sur la réussite des étudiants.
Il est essentiel pour les préparer au monde professionnel, où la capacité à recevoir et à intégrer des critiques constructives est indispensable. Le feedback est une des clefs de voute dans notre approche de l’évaluation par les pairs.
Chez ChallengeMe, on observe différents types de feedback. Pour être efficace, le feedback doit être varié et adapté aux besoins spécifiques des étudiants. Voici quelques types de feedback que nous observons régulièrement:
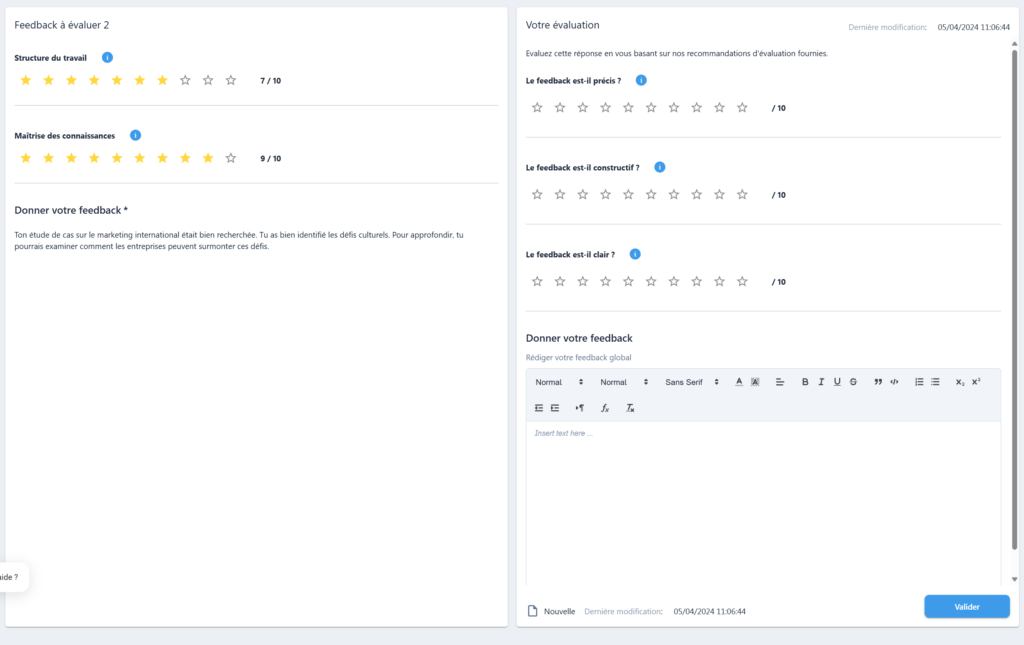
.Le choix judicieux des critères d’évaluation est fondamental pour un feedback efficace. Ces critères servent de guide tant pour les évaluateurs que pour les évalués, assurant ainsi une cohérence et une pertinence dans le processus de feedback.
Dans la mesure du possible, les critères d’évaluation doivent être:
Impliquer les étudiants dans le processus de définition des critères peut augmenter leur engagement et leur compréhension :
N’hésitez pas à jeter un œil à nos rubriques de critères disponibles ici:

Le rétro-feedback, également connu sous le nom de feedback sur le feedback ou encore back-feedback, est une pratique pédagogique avancée qui ajoute une couche supplémentaire de réflexion au processus d’évaluation par les pairs. Cette approche permet aux étudiants d’analyser et d’évaluer la qualité des retours qu’ils reçoivent et donnent, créant ainsi une boucle d’apprentissage plus profonde et plus riche.
Chez ChallengeMe, nous avons créer une phase dédiée pour ce type de feedback. Vous pouvez définir des critères d’évaluation (n’hésitez pas à utiliser notre banque de critères).
Le rétro-feedback est un outil puissant pour approfondir l’apprentissage et développer des compétences critiques en matière d’évaluation et de communication. Les bénéfices en termes de développement des compétences métacognitives et d’amélioration de la qualité globale du feedback en font une pratique précieuse dans l’enseignement supérieur.
Un environnement d’apprentissage qui valorise le feedback est essentiel. Les erreurs doivent être perçues comme des opportunités d’apprentissage, et non comme des échecs. Encourager les étudiants à voir le feedback comme un outil de développement personnel peut transformer leur expérience éducative.
Préparer les étudiants au feedback est essentiel pour maximiser son impact sur leur apprentissage. Commencez par expliquer l’importance du feedback dans le processus d’apprentissage, en soulignant qu’il s’agit d’un outil puissant pour le développement personnel et professionnel, et non d’une simple critique. Enseignez aux étudiants les principes d’un feedback constructif. Cela inclut l’importance d’être spécifique, objectif et orienté vers l’action. Encouragez-les à se concentrer sur les comportements et les résultats plutôt que sur les personnes, et à proposer des suggestions concrètes d’amélioration.
Pour approfondir ce sujet, nous vous invitons à visionner notre vidéo explicative qui aborde en détail les techniques pour donner et recevoir un feedback efficace. Cette ressource offre des conseils pratiques et des exemples concrets pour aider les étudiants à maîtriser cet aspect crucial de leur développement académique et professionnel.
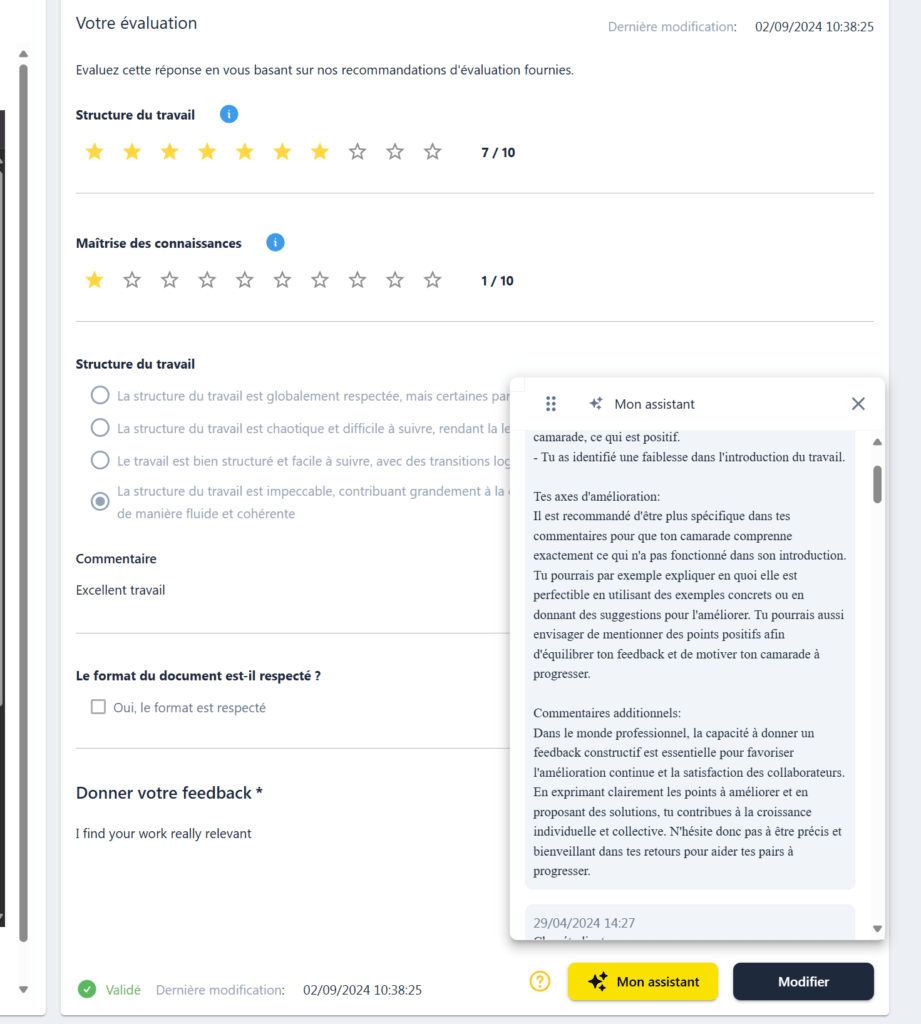
L’intelligence artificielle (IA) joue un rôle de plus en plus important dans l’amélioration du feedback académique, et ChallengeMe intègre ces avancées pour enrichir l’expérience d’apprentissage des étudiants. En tant qu’assistant au feedback, l’IA peut synthétiser les notes et les commentaires reçus par un étudiant, offrant ainsi une vue d’ensemble claire de ses performances et de ses progrès. Cette synthèse aide les étudiants à identifier rapidement les domaines nécessitant une attention particulière, tout en mettant en évidence leurs points forts. En facilitant une compréhension globale du feedback, l’IA permet aux étudiants de mieux orienter leurs efforts d’amélioration.
De plus, l’IA peut assister les étudiants dans la rédaction de leurs propres feedbacks, en leur fournissant des suggestions pour améliorer la pertinence et la constructivité de leurs commentaires. Par exemple, l’IA peut analyser le feedback que les étudiants rédigent et proposer des améliorations en temps réel. Ces suggestions peuvent inclure des conseils sur la spécificité, l’équilibre entre les critiques et les encouragements, et l’évitement des jugements personnels.
En intégrant ces fonctionnalités, ChallengeMe aide les étudiants à développer des compétences essentielles en communication critique, tout en allégeant la charge des enseignants en matière de supervision et de correction des feedbacks. L’IA devient ainsi un partenaire précieux dans la création d’un environnement d’apprentissage plus efficace et personnalisé.
Pour ceux qui souhaitent explorer davantage le sujet du feedback, plusieurs ressources et experts offrent des perspectives enrichissantes :
En adoptant ces bonnes pratiques et en s’appuyant sur les ressources disponibles, les enseignants peuvent transformer le feedback en un puissant levier d’apprentissage. En fin de compte, le feedback n’est pas seulement une rétroaction, mais un dialogue continu qui enrichit l’expérience éducative et prépare les étudiants à réussir dans leurs futures carrières.